The Truth About Red Light Cameras: Safety or Revenue?
Red light cameras have sparked intense debate since their introduction at busy intersections worldwide. Supporters claim these cameras are essential tools for enhancing traffic safety, while critics argue they exist mainly to generate revenue for local governments. So, what is the truth behind red light cameras? Are they genuinely improving safety, or are they primarily cash machines? This article explores both sides of the debate, supported by data and expert opinions, to help you understand the reality of red light cameras.
What Are Red Light Cameras and How Do They Work?
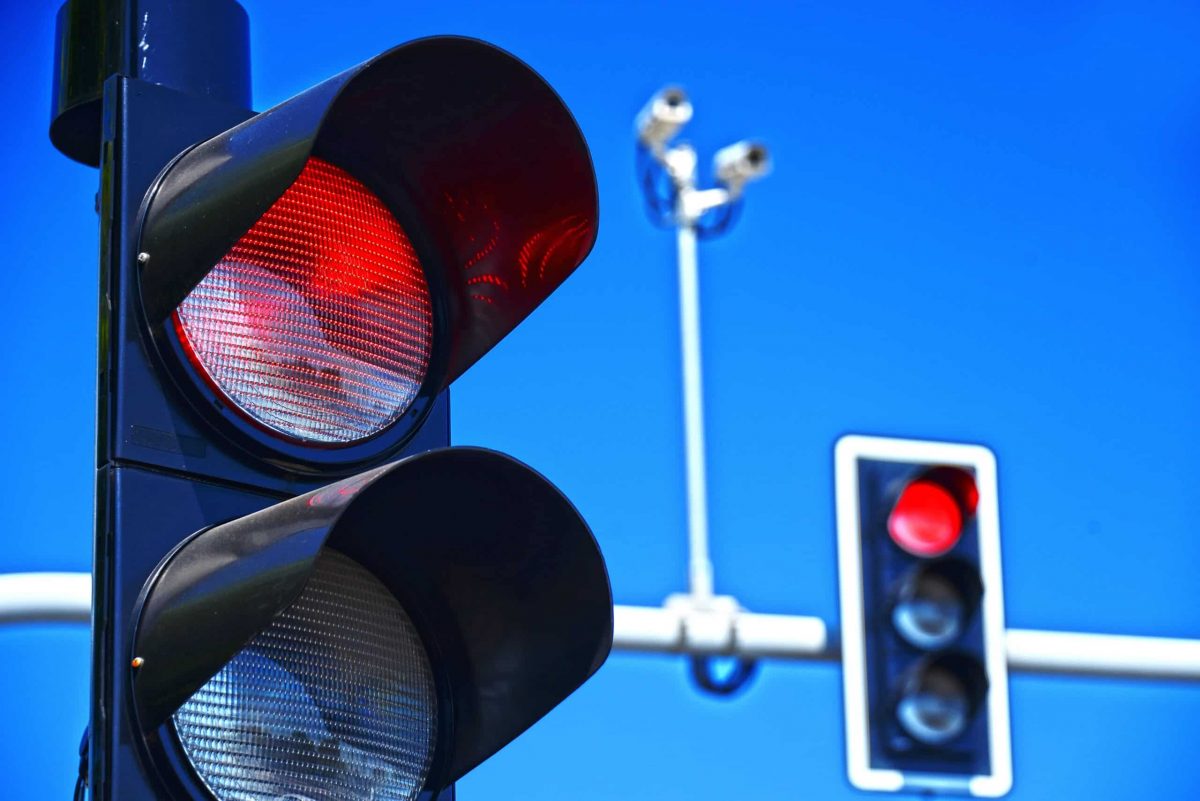
Before diving into the controversy, it’s important to understand what red light cameras are and how they function. These automated devices are installed at intersections to detect and photograph vehicles running red lights. Equipped with sensors and cameras, they capture evidence of violations that lead to citations being mailed to the vehicle’s registered owner.
Technology Behind Red Light Cameras
Red light cameras operate using induction loops or radar sensors embedded in the pavement, which detect when a vehicle crosses the stop line after the light has turned red. Once triggered, the system takes high-resolution photos or videos showing the vehicle in violation, including license plate details, the traffic signal phase, date, time, and location.
Red Light Cameras and Traffic Safety: What the Data Shows
One of the strongest arguments in favor of red light cameras is their potential to improve road safety. Various studies have investigated whether these cameras effectively reduce accidents and save lives.
Reduction in Side-Impact Collisions
Research indicates that red light cameras significantly reduce T-bone or side-impact collisions, which tend to be severe and cause serious injuries or fatalities. According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), intersections with red light cameras have experienced up to a 25% decrease in these types of crashes.
Mixed Impact on Rear-End Collisions
However, the data also shows a more complex picture. While side-impact crashes decrease, some studies report an increase in rear-end collisions at intersections equipped with red light cameras. This happens because some drivers abruptly stop when the light turns yellow to avoid running a red light, leading to more rear-end crashes. Despite this, rear-end collisions generally result in less severe injuries compared to side-impact crashes.
Overall Impact on Traffic Fatalities
Meta-analyses combining multiple studies have found that red light cameras contribute to an overall reduction in traffic fatalities. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) estimates that widespread use of red light cameras could prevent thousands of deaths annually in the United States alone.
The Revenue Side of Red Light Cameras
Despite clear safety benefits, red light cameras also generate significant revenue for municipalities, raising concerns about potential conflicts of interest.
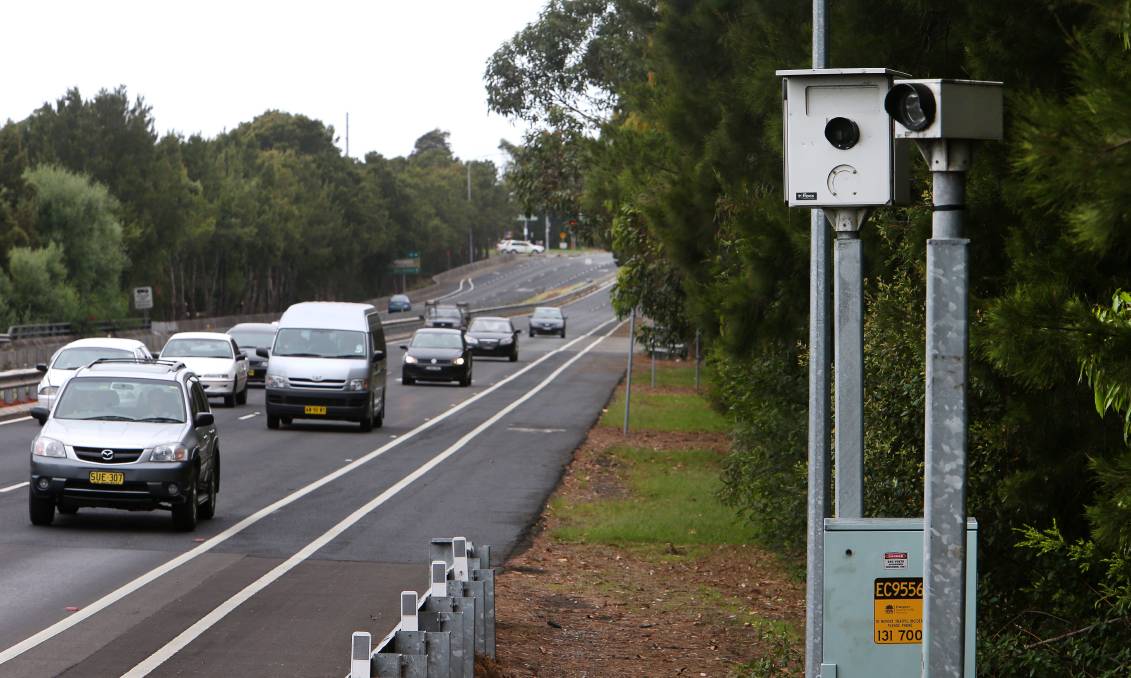
How Much Revenue Do Red Light Cameras Generate?
Red light camera fines often cost drivers between $50 and $150 per violation, depending on the jurisdiction. In many cities, cameras are responsible for millions of dollars in annual revenue. For example, in some large urban areas, red light camera programs generate tens of millions each year, which supports local government budgets.
Are Cameras Primarily Installed for Revenue?
This question fuels much of the skepticism around red light cameras. Critics argue that some jurisdictions prioritize installing cameras at locations that produce the highest ticket volume rather than areas with the most dangerous intersections. Additionally, there have been cases where cameras remained in place long after accident rates dropped, suggesting a revenue-driven motive.
Use of Revenue from Fines
Many cities reinvest red light camera revenue into transportation safety programs, infrastructure improvements, or public awareness campaigns. However, transparency varies, and in some cases, funds are absorbed into general budgets, which reduces public trust.
Legal and Ethical Concerns
The use of red light cameras raises important legal and ethical questions, especially related to due process and fairness.
Due Process and Ticketing
Red light camera tickets are typically issued to the vehicle owner, regardless of who was driving at the time of the violation. Critics argue that this can violate the principle of “innocent until proven guilty,” as owners must prove they were not driving or pay the fine regardless. Some jurisdictions offer options to contest tickets, but the burden often falls on the vehicle owner.
Privacy Concerns
Another issue is the privacy implications of constant surveillance. Opponents worry about the extent of monitoring and data collection on drivers’ movements, with some fearing misuse or lack of safeguards surrounding image storage and access.
Public Opinion on Red Light Cameras
Public attitudes towards red light cameras are divided and can vary widely depending on local experiences and enforcement practices.
Supporters of Red Light Cameras
Many drivers and safety advocates support cameras as a necessary deterrent that promotes safer driving habits and reduces accidents. They view the cameras as an impartial, consistent way to enforce traffic laws and save lives.
Critics and Opposition
Opponents often see red light cameras as unfair, revenue-driven, and prone to errors or misuse. Some local communities have successfully campaigned to remove or ban red light cameras, citing concerns over fairness and civil liberties.
The Future of Red Light Cameras: Balancing Safety and Fairness
As technology advances, so does the potential for smarter and fairer traffic enforcement.
AI and Improved Accuracy
Future red light camera systems may use artificial intelligence to more accurately identify violations, reduce false tickets, and even distinguish between different types of vehicles and traffic situations.
Enhanced Transparency and Accountability
There is increasing demand for clearer policies on how camera-generated revenue is used and improved procedures for contesting tickets, ensuring fairness for drivers.
Integration with Broader Traffic Safety Programs
Red light cameras are likely to become part of integrated smart traffic systems that dynamically manage traffic flow while enforcing laws, further enhancing road safety.
Conclusion
The truth about red light cameras is complex. While they undoubtedly contribute to reducing dangerous side-impact collisions and saving lives, they also serve as significant revenue sources for many municipalities. Concerns about fairness, privacy, and potential revenue-driven motives persist. For red light cameras to gain broader acceptance, transparency, technological improvements, and balanced policies that prioritize safety over revenue are essential.
Ultimately, understanding both sides of the debate can help drivers and policymakers make informed decisions about the role of red light cameras in our transportation systems.